The cybercrime landscape has witnessed a seismic shift with the emergence of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS), transforming ransomware attacks into a lucrative industry. In 2025, RaaS continues to dominate the digital threat arena, empowering cybercriminals with easy-to-use tools and comprehensive services to execute devastating attacks.
This article explores the growth of RaaS, its operational model, the implications for businesses and individuals, and strategies to safeguard against this pervasive threat.
What is Ransomware-as-a-Service?
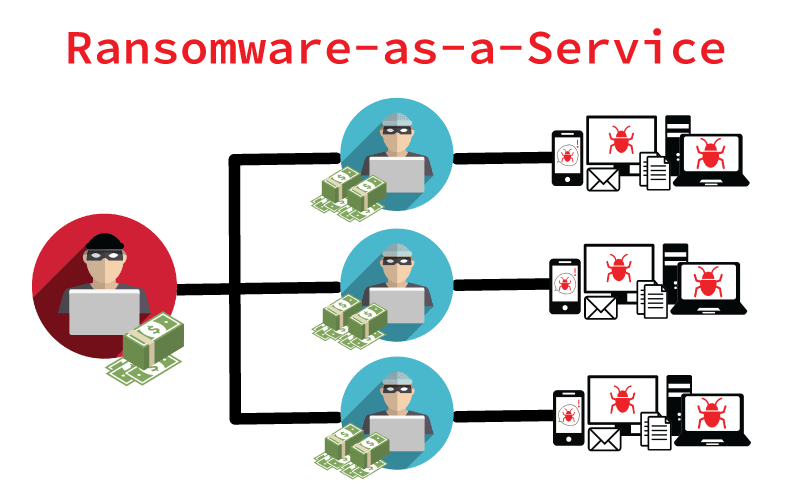
Ransomware-as-a-Service refers to a subscription-based model where cybercriminals provide ready-to-deploy ransomware tools and services to other attackers, often referred to as “affiliates.” This business model mimics legitimate software-as-a-service (SaaS) platforms, complete with user-friendly interfaces, technical support, and revenue-sharing agreements.
RaaS lowers the entry barrier for aspiring cybercriminals, enabling even those with limited technical expertise to launch sophisticated ransomware campaigns.
The Growth of Ransomware-as-a-Service
In 2025, the rise of RaaS can be attributed to several factors:
1. Lucrative Revenue Model
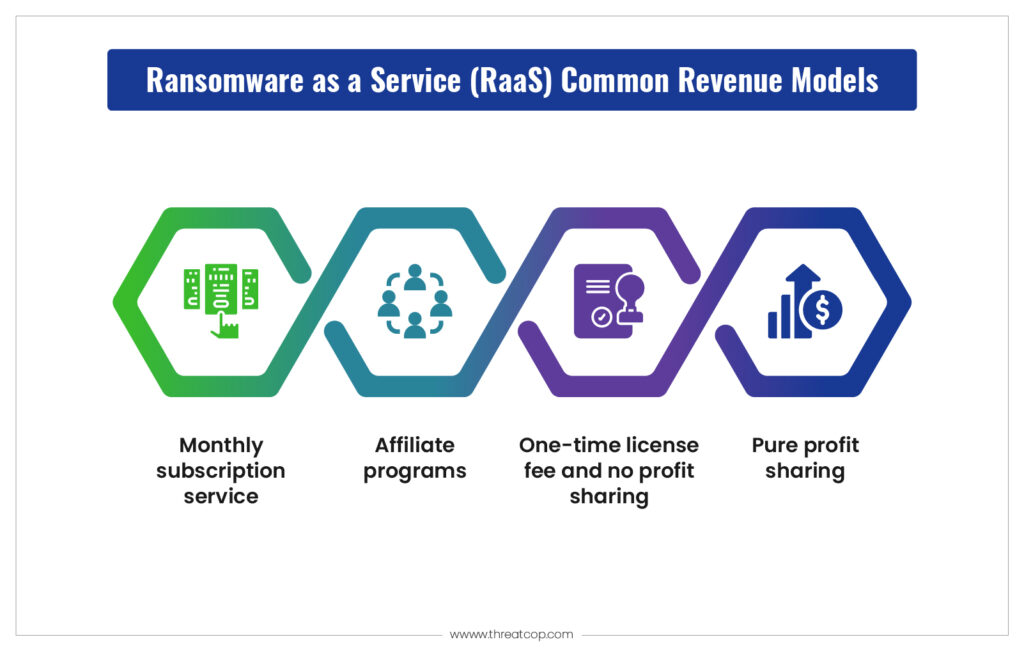
Ransomware groups share profits with affiliates, typically splitting earnings in ratios like 70/30 or 80/20. This incentivizes affiliates to participate and scale operations.
2. Accessibility and Anonymity
The dark web hosts numerous RaaS marketplaces, providing anonymity for buyers and sellers. Cryptocurrency payments further obscure financial transactions.
3. Advanced Features
Modern RaaS platforms include features like:
- Customizable payloads
- Built-in encryption algorithms
- Real-time dashboards to track infections and payments
4. Increased Target Diversity
RaaS enables attackers to target a wide array of victims, from small businesses to critical infrastructure, creating widespread havoc.
RaaS Operations: How It Works
RaaS providers manage the backend operations, while affiliates handle the front-end deployment. Here’s a breakdown of the RaaS workflow:
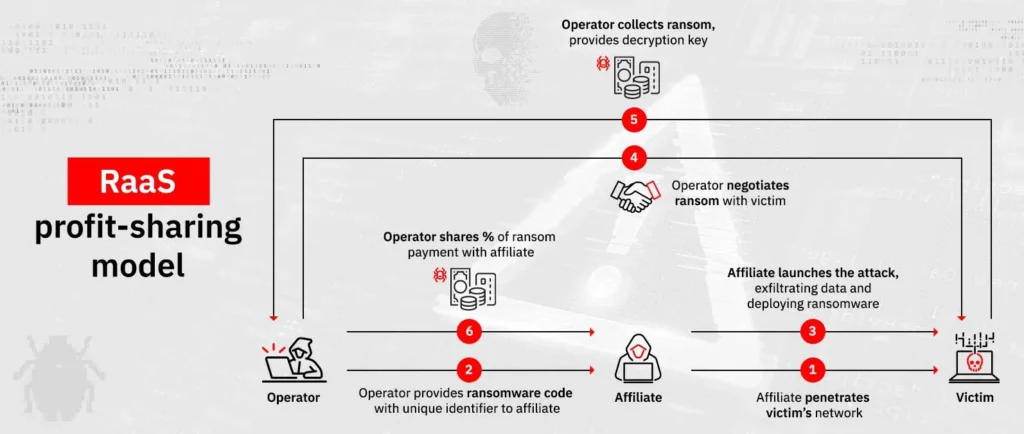
1. Development and Distribution
Providers create ransomware software and sell or lease it on dark web forums.
2. Affiliate Recruitment
RaaS platforms advertise to potential affiliates, offering attractive revenue-sharing terms.
3. Attack Execution
Affiliates deploy ransomware through phishing emails, malicious ads, or exploiting software vulnerabilities.
4. Payment and Revenue Sharing
Victims pay ransom through cryptocurrency, which is divided between the affiliate and the provider.
Notable RaaS Groups in 2025
Several RaaS groups have gained notoriety for their high-profile attacks:

Conti RaaS
Known for its aggressive tactics, Conti has targeted governments, healthcare providers, and large corporations.

LockBit 3.0
This group offers customization options, allowing affiliates to tailor ransomware to specific targets.

REvil (Sodinokibi)
A re-emergent player in 2025, REvil provides 24/7 support and extensive resources for affiliates.
Impact of Ransomware-as-a-Service
1. Increased Ransomware Attacks
The accessibility of RaaS has led to a surge in ransomware incidents, overwhelming cybersecurity defenses globally.
2. Escalating Ransom Demands
Victims are facing higher ransom demands, often in the millions, as RaaS groups target wealthier organizations.
3. Threat to Critical Infrastructure
RaaS attacks on utilities, transportation, and healthcare systems pose risks to public safety and national security.
4. Economic Consequences
The global economy suffers losses in the billions annually due to ransom payments, downtime, and recovery costs.
Defending Against Ransomware-as-a-Service
1. Strengthen Cyber Hygiene
- Regularly update software and patch vulnerabilities.
- Implement robust password policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
2. Invest in Employee Training
Train employees to recognize phishing attempts and avoid clicking on suspicious links or attachments.
3. Deploy Advanced Security Tools
Use endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, firewalls, and anti-ransomware software to detect and block attacks.
4. Regular Backups
Maintain encrypted backups of critical data and store them offline.
5. Incident Response Plan
Develop and test a comprehensive incident response plan to minimize downtime and data loss.
6. Engage Cybersecurity Experts
Partner with cybersecurity firms for threat monitoring and vulnerability assessments.
Ransomware-as-a-Service represents a growing threat to cybersecurity in 2025, turning ransomware attacks into an accessible and profitable enterprise for cybercriminals. Businesses and individuals must adopt proactive measures to defend against this evolving menace. By investing in strong cybersecurity practices, fostering awareness, and leveraging advanced tools, organizations can mitigate the risks posed by RaaS and ensure resilience in an increasingly digital world.
FAQs
What is the Ransomware-as-a-Service model?
Ransomware-as-a-Service is a subscription-based platform where cybercriminals provide ransomware tools and services to affiliates for executing attacks.
Why has Ransomware-as-a-Service grown in 2025?
Its growth is fueled by accessibility, lucrative revenue-sharing models, and advanced features that attract affiliates with varying skill levels.
How can businesses protect against Ransomware-as-a-Service?
Businesses can protect themselves by updating systems, training employees, using robust security tools, and maintaining secure backups.
What industries are most affected by RaaS?
Critical infrastructure, healthcare, finance, and small to medium-sized enterprises are frequently targeted by RaaS operations.
Are there any legal consequences for RaaS operators?
Yes, international law enforcement agencies are actively dismantling RaaS networks and prosecuting operators and affiliates.
How do RaaS groups recruit affiliates?
RaaS groups use dark web forums and encrypted communication channels to attract affiliates, often showcasing success stories and revenue potential.