The quest for sustainable energy solutions has positioned green hydrogen as a cornerstone in the global energy transition. Produced using renewable energy and water, green hydrogen is a versatile and carbon-free energy carrier with the potential to decarbonize hard-to-abate sectors such as heavy industry and transportation. As governments and private sectors ramp up investments in hydrogen, its expansion promises to revolutionize energy systems and accelerate the shift toward a net-zero future.
What Is Green Hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is produced through electrolysis, a process that splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity from renewable sources like solar or wind. Unlike grey hydrogen (produced from natural gas) or blue hydrogen (which uses carbon capture), green hydrogen is entirely carbon-free.
- Key Characteristics:
- Carbon-neutral production process
- Flexible energy carrier, usable in various applications
- Long-term storage capabilities
Its versatility and eco-friendly credentials make green hydrogen a critical component of the global energy mix.

Why Is Green Hydrogen Crucial for a Sustainable Future?
Green hydrogen addresses several challenges in the transition to clean energy:
- Decarbonizing Hard-to-Abate Sectors: Industries like steel, cement, and chemicals can use green hydrogen to replace fossil fuels.
- Energy Storage and Transport: Hydrogen can store excess renewable energy and transport it across long distances.
- Zero-Emission Mobility: Fuel cell vehicles powered by hydrogen offer a clean alternative for heavy transport, shipping, and aviation.
As countries aim for net-zero emissions, green hydrogen provides a pathway to tackle emissions that other renewable technologies cannot easily address.
Global Investments in Green Hydrogen
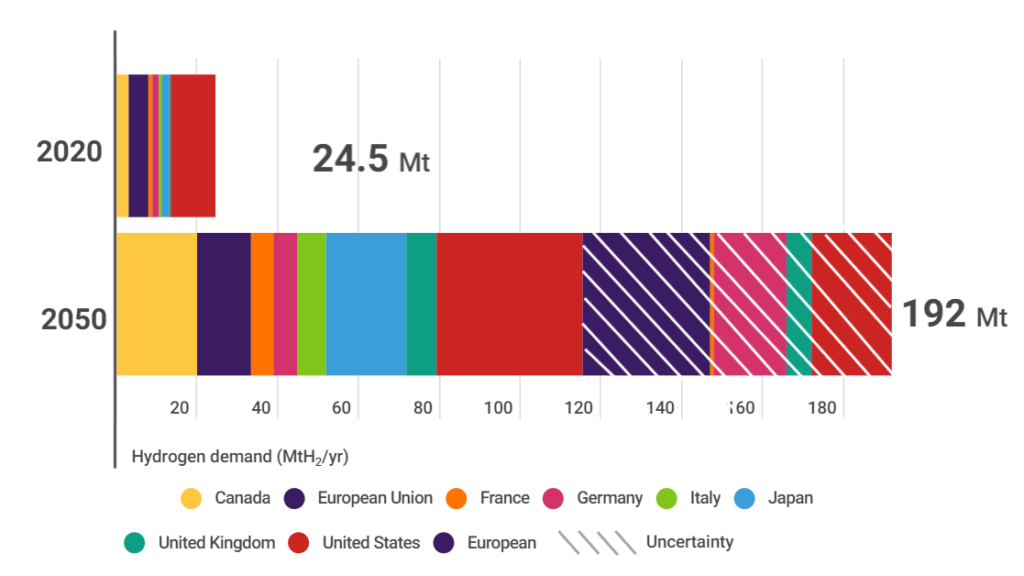
The push for green hydrogen has triggered unprecedented levels of investment from both public and private sectors.
Government Initiatives and Policies
- European Union: Plans to invest €470 billion in green hydrogen by 2050 through its Hydrogen Strategy.
- United States: The Inflation Reduction Act allocates substantial tax credits and funding for green hydrogen projects.
- Japan and South Korea: Leaders in hydrogen technology development, aiming for hydrogen-centric economies by 2050.
Private Sector Commitments
- Major corporations, including BP, Shell, and Siemens, are investing in green hydrogen production facilities and infrastructure.
- Venture capital is flowing into startups innovating in electrolyzer technology and hydrogen storage solutions.
These investments aim to scale up production, reduce costs, and create a robust global hydrogen supply chain.
Challenges to Green Hydrogen Expansion

While the potential of green hydrogen is immense, several barriers must be addressed:
- High Production Costs: Electrolyzers and renewable energy contribute to the high cost of green hydrogen, making it less competitive than fossil fuels.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Widespread adoption requires investments in pipelines, refueling stations, and storage facilities.
- Energy Efficiency Losses: The energy conversion process in electrolysis and fuel cells is less efficient compared to direct electricity use.
- Policy and Regulation: Harmonized global standards and incentives are needed to accelerate adoption.
Technological Innovations Driving Green Hydrogen Growth

Technological advancements are critical for reducing costs and improving the scalability of green hydrogen:
- Next-Generation Electrolyzers: Research into proton exchange membrane (PEM) and solid oxide electrolyzers aims to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Hydrogen Storage Solutions: Innovations in solid-state storage and liquid hydrogen transportation are addressing storage challenges.
- AI and IoT Integration: Optimizing production and distribution processes through smart systems.
These innovations will play a key role in making green hydrogen economically viable.
Key Applications of Green Hydrogen
Green hydrogen’s versatility enables its application across multiple sectors:
- Industry:
- Replacing coke in steel production.
- Decarbonizing chemical manufacturing processes.
- Energy Storage:
- Balancing intermittent renewable energy sources by storing surplus power.
- Transport:
- Fueling hydrogen-powered trucks, buses, trains, and ships.
- Power Generation:
- Hydrogen turbines and fuel cells provide a clean alternative for power plants.
- Residential and Commercial Use:
- Blending hydrogen into natural gas pipelines for heating and cooking.
The Economic and Environmental Impact of Green Hydrogen
Economic Growth

- Creation of new industries and jobs, especially in manufacturing, infrastructure development, and R&D.
- Stimulation of local economies through renewable energy projects powering electrolyzers.
Environmental Benefits
- Significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
- Improved air quality due to zero-emission transportation and industrial processes.
Green hydrogen’s dual role in economic development and environmental stewardship makes it a cornerstone of sustainable progress.
Future Trends in Green Hydrogen Expansion
- Cost Reduction Through Economies of Scale:
Large-scale projects and increased competition will drive down production costs. - Hydrogen Hubs and Export Markets:
Countries rich in renewable energy resources, such as Australia and the Middle East, are positioning themselves as global hydrogen exporters. - Sector Coupling:
Integrating hydrogen with other renewable technologies, such as solar and wind farms, to maximize efficiency. - Carbon-Free Hydrogen Certification:
Certifications will ensure transparency and market confidence in green hydrogen’s environmental credentials.
The expansion of green hydrogen represents a monumental step in the transition to a sustainable and resilient energy system. As investments pour into production technologies, infrastructure, and innovative applications, green hydrogen is poised to bridge gaps that other renewables cannot fill.
Its potential to decarbonize heavy industries, stabilize energy supplies, and fuel zero-emission transport makes it a critical pillar of global climate strategies. While challenges remain, the combined efforts of governments, industries, and researchers are paving the way for green hydrogen to power a cleaner, greener future.
FAQs
What is green hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is a clean energy carrier produced through electrolysis using renewable energy, resulting in zero carbon emissions.
Why is green hydrogen important for decarbonization?
It enables the decarbonization of sectors like heavy industry, transportation, and power generation, which are challenging to electrify.
What challenges does green hydrogen face?
High production costs, lack of infrastructure, energy efficiency losses, and the need for supportive policies are key challenges.
How is the cost of green hydrogen being reduced?
Technological advancements in electrolyzers, scaling up production, and government incentives are driving cost reductions.
Which countries are leading the green hydrogen revolution?
The European Union, United States, Japan, South Korea, and Australia are at the forefront of green hydrogen development.
Can green hydrogen be used for energy storage?
Yes, green hydrogen can store excess renewable energy and provide backup power during low-generation periods.