As businesses become increasingly interconnected, third-party vendors, suppliers, and partners play critical roles in operations. However, with this reliance comes significant risks. Third-party risks—vulnerabilities stemming from external entities—pose serious challenges to cybersecurity in 2025. From supply chain attacks to data breaches, these risks can have far-reaching consequences. Building resilient cyber partnerships is no longer optional; it is imperative for safeguarding businesses in a complex threat landscape.
Understanding Third-Party Risks

Third-party risks refer to vulnerabilities introduced into an organization through its reliance on external entities. These entities often have access to sensitive data or systems, making them potential entry points for cyberattacks.
- Types of Third-Party Risks:
- Operational Risks: Disruptions in service delivery due to cyber incidents affecting a vendor.
- Data Privacy Risks: Breaches resulting from mishandling or theft of sensitive data by third parties.
- Compliance Risks: Non-compliance with regulations due to vendor-related vulnerabilities.
- Reputational Risks: Damage to an organization’s reputation due to third-party failures.
Why Are Third-Party Risks Increasing in 2025?
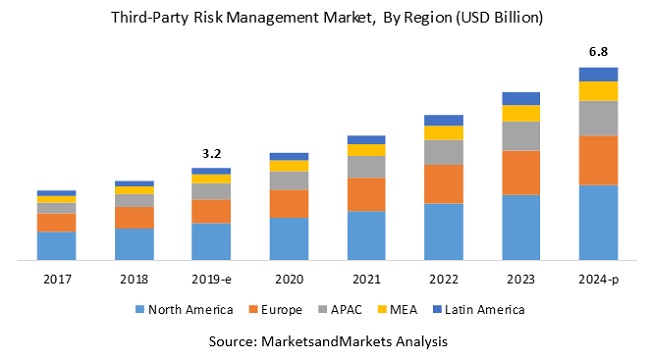
The evolving technological and geopolitical landscape amplifies third-party risks. Several factors contribute to this trend:
- Expansion of Supply Chains: Globalized and digitally reliant supply chains introduce vulnerabilities at every link.
- Proliferation of SaaS Providers: Increasing reliance on cloud-based services and applications elevates risk exposure.
- Sophistication of Threat Actors: Cybercriminals target third parties as soft entry points into larger organizations.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Stricter regulations demand accountability for third-party cybersecurity practices.
In 2025, organizations must address these challenges through proactive strategies and stronger partnerships.
High-Profile Third-Party Attacks: Lessons Learned
Notable third-party attacks highlight the devastating consequences of unmitigated risks:

- SolarWinds (2020): A supply chain attack affecting thousands of organizations globally, including government agencies.
- Kaseya Ransomware (2021): Hackers exploited Kaseya’s remote management software, impacting hundreds of companies.
- MOVEit File Transfer Breach (2023): A vulnerability in a file transfer tool led to sensitive data exposure for multiple clients.
These incidents underscore the need for robust risk management and the importance of assessing vendor cybersecurity.
Key Challenges in Managing Third-Party Risks
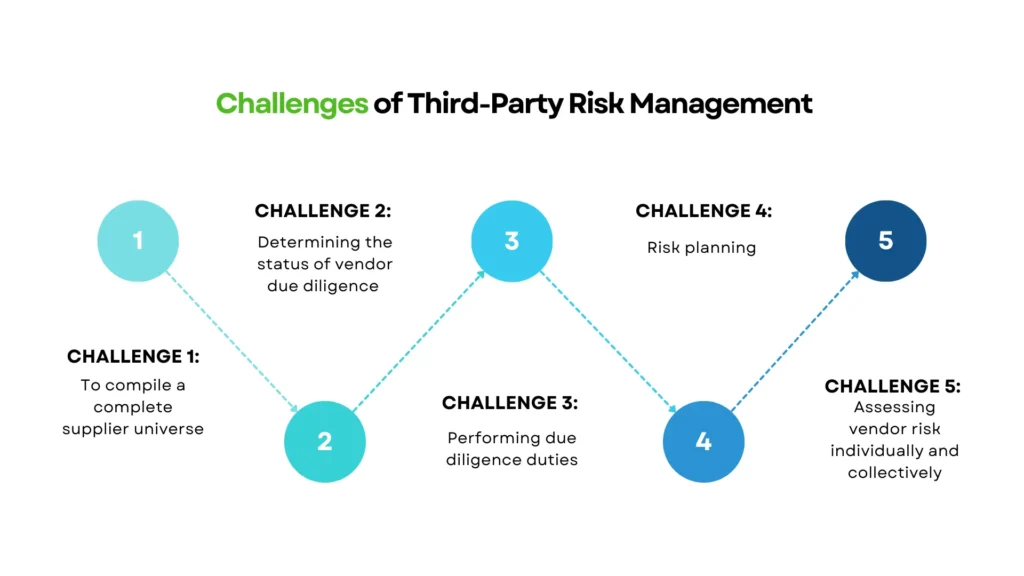
Addressing third-party risks is complex due to:
- Lack of Visibility: Many organizations lack insight into their vendors’ cybersecurity practices.
- Resource Constraints: Smaller companies often lack the resources to evaluate and monitor third-party risks effectively.
- Dynamic Threat Landscape: Threat actors continually innovate, making it challenging to anticipate risks.
- Inconsistent Standards: Vendors operate under varying levels of cybersecurity maturity, creating gaps in protection.
Building Resilient Cyber Partnerships in 2025

Resilient cyber partnerships involve collaborative approaches to managing third-party risks. This includes setting clear expectations, fostering trust, and ensuring accountability.
- Steps to Build Resilient Partnerships:
- Vendor Risk Assessments: Conduct thorough evaluations before onboarding vendors.
- Cybersecurity Standards: Establish clear security requirements and SLAs for all third-party partners.
- Continuous Monitoring: Use tools to track vendor compliance and detect anomalies in real-time.
- Incident Response Planning: Develop joint response strategies for handling breaches involving third parties.
- Transparent Communication: Foster open channels for reporting incidents and sharing threat intelligence.
Technologies for Managing Third-Party Risks in 2025
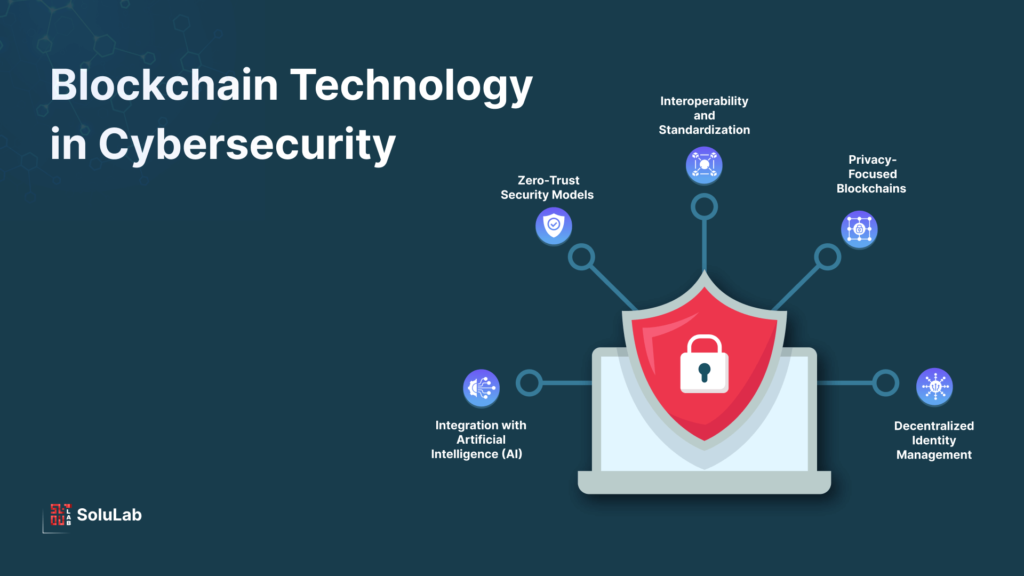
Innovative technologies are essential for addressing the growing complexities of third-party risks.
- AI-Powered Risk Management: Automates the analysis of vendor behavior and flags potential vulnerabilities.
- Blockchain for Supply Chain Security: Enhances traceability and ensures data integrity across supply chains.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Monitors cloud environments for misconfigurations that third parties might exploit.
- Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) Platforms: Centralize vendor assessments and compliance tracking.
Best Practices for Mitigating Third-Party Risks
To effectively manage third-party risks, organizations must adopt a proactive and structured approach:

- Map the Supply Chain: Identify all third-party relationships and prioritize critical dependencies.
- Implement Multi-Layered Security: Combine endpoint security, encryption, and access controls to protect sensitive data.
- Conduct Cybersecurity Audits: Periodically assess vendor security practices and identify gaps.
- Adopt Zero Trust Principles: Verify every user, device, and application accessing your systems, including third-party connections.
- Train Staff on Third-Party Risks: Educate employees about recognizing potential vulnerabilities and ensuring secure interactions with vendors.
The Role of Regulations in Third-Party Risk Management
Governments and regulatory bodies are intensifying their focus on third-party risks:
- Key Regulations in 2025:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Expands accountability for third-party data breaches.
- NIST Supply Chain Risk Management Practices: Provides guidance on mitigating third-party risks in supply chains.
- Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC): Enforces third-party cybersecurity standards for federal contractors in the U.S.
Compliance with these frameworks is not just a legal obligation; it also enhances resilience against threats.
Future Trends in Third-Party Risk Management

The future of managing third-party risks lies in innovation, collaboration, and adaptability:
- Risk Intelligence Sharing: Organizations will increasingly share threat intelligence within industries to enhance collective defenses.
- Cyber Resilience Benchmarks: Standardized metrics will emerge to measure and compare vendor security maturity.
- Automated Vendor Assessments: AI-driven tools will streamline the evaluation of vendor risks.
- Focus on Micro-Supply Chains: Companies will manage smaller, localized supply chains to reduce exposure.
In 2025, the ability to manage third-party risks will define an organization’s cybersecurity resilience. By fostering resilient cyber partnerships, companies can mitigate vulnerabilities, comply with regulations, and maintain trust in an increasingly interconnected world. Investing in advanced technologies, proactive strategies, and collaborative efforts will ensure that third-party relationships remain an asset, not a liability, in the fight against cyber threats.
FAQs
What are third-party risks?
Third-party risks are vulnerabilities that arise from a company’s reliance on external vendors, suppliers, or partners, potentially leading to data breaches or operational disruptions.
Why are third-party risks significant in 2025?
Increased digitalization, interconnected supply chains, and evolving cyber threats make third-party risks a critical concern for businesses in 2025.
How can organizations assess third-party risks?
Organizations can conduct vendor risk assessments, audit cybersecurity practices, and monitor compliance using TPRM platforms.
What is the role of Zero Trust in mitigating third-party risks?
Zero Trust principles ensure constant verification of third-party access, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized intrusions.
Are there technologies to manage third-party risks?
Yes, AI-powered risk management tools, blockchain for data integrity, and CSPM platforms are crucial technologies for managing third-party risks.
What happens if a third party causes a data breach?
Organizations may face regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and financial losses, highlighting the importance of effective third-party risk management.